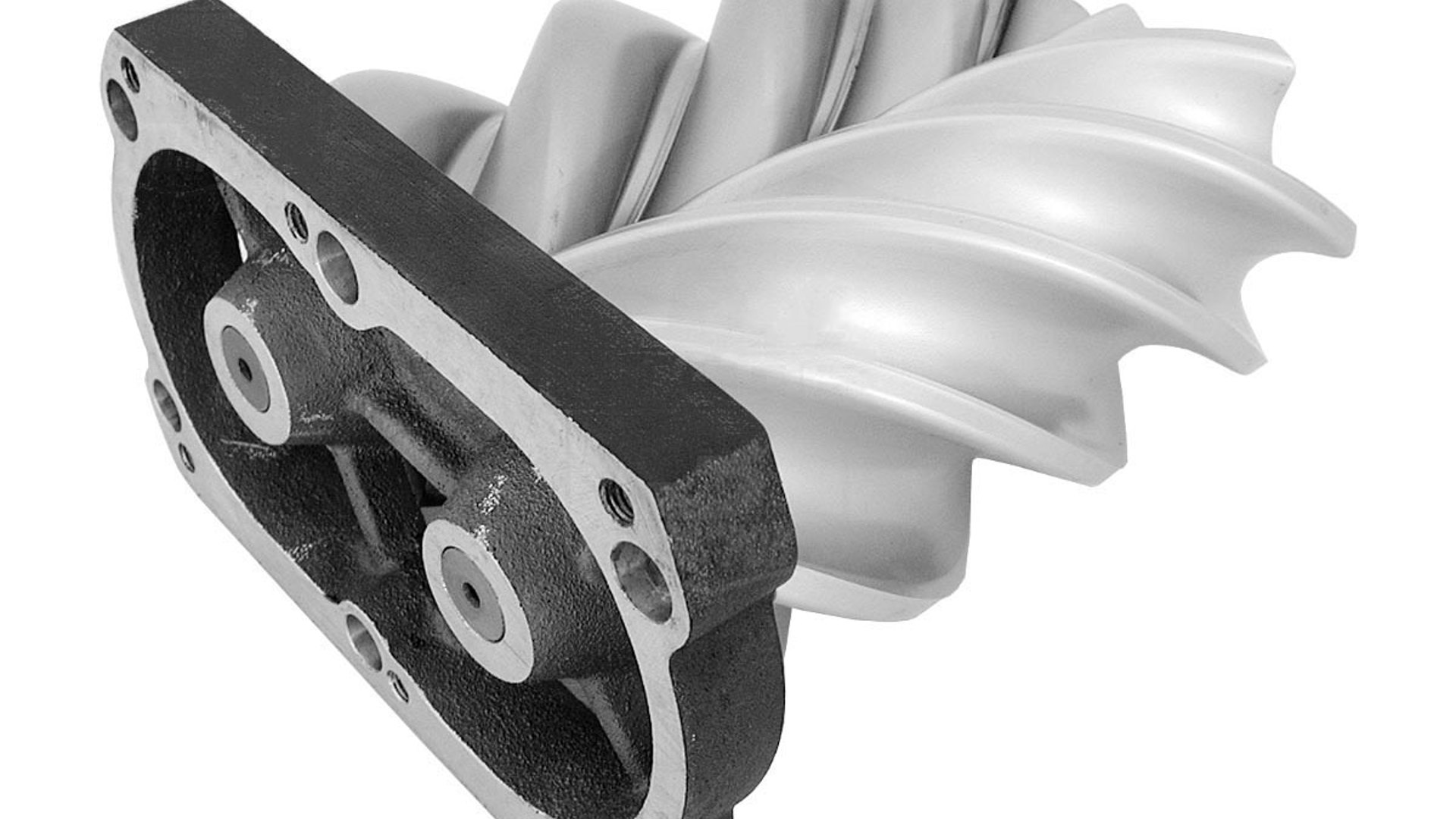
Answering the call of shoppers after higher performance and reduced fuel consumption, more and more automakers are shifting to boosted small-displacement engines to deliver a high-performance, high-efficiency punch.
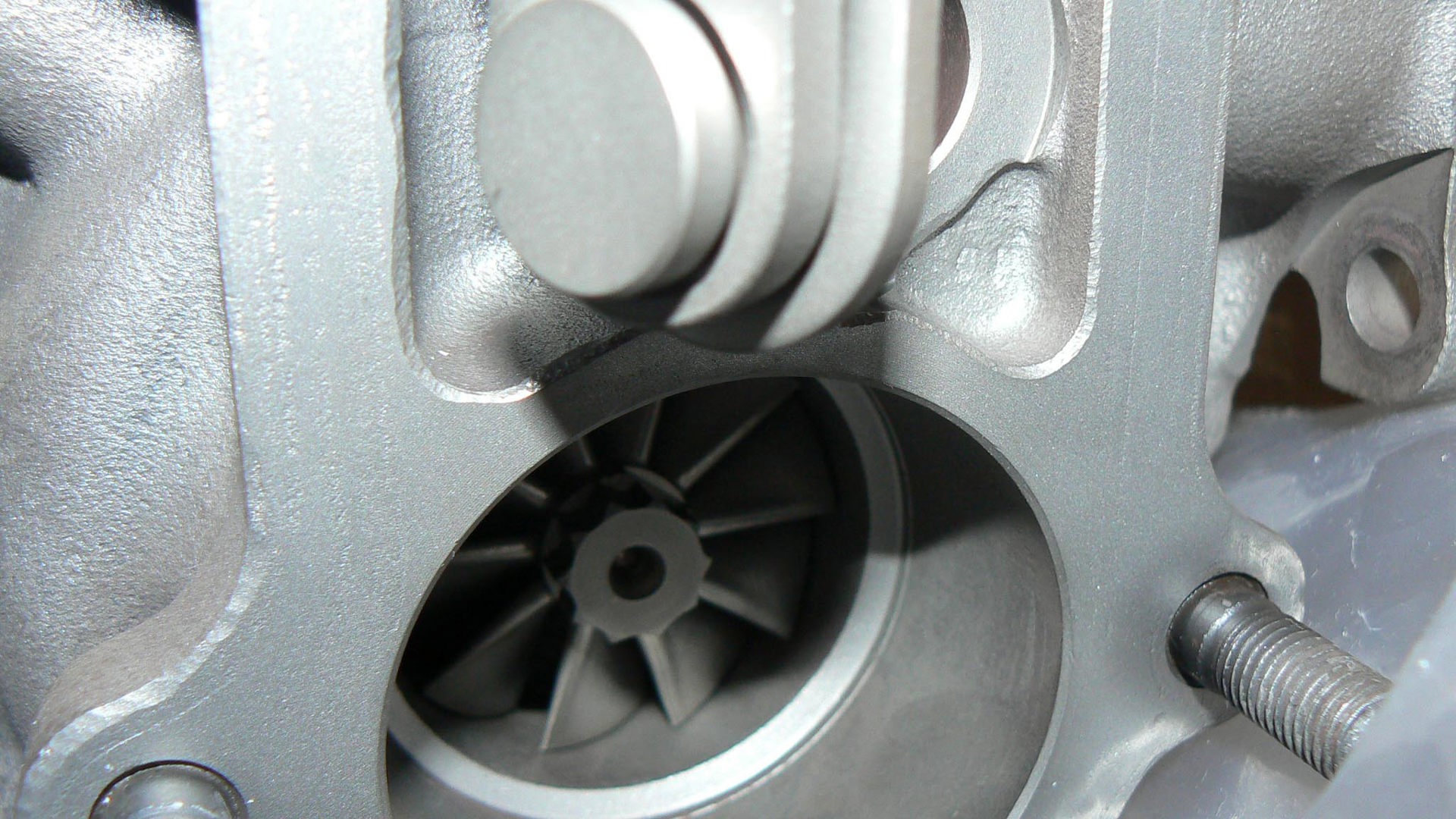
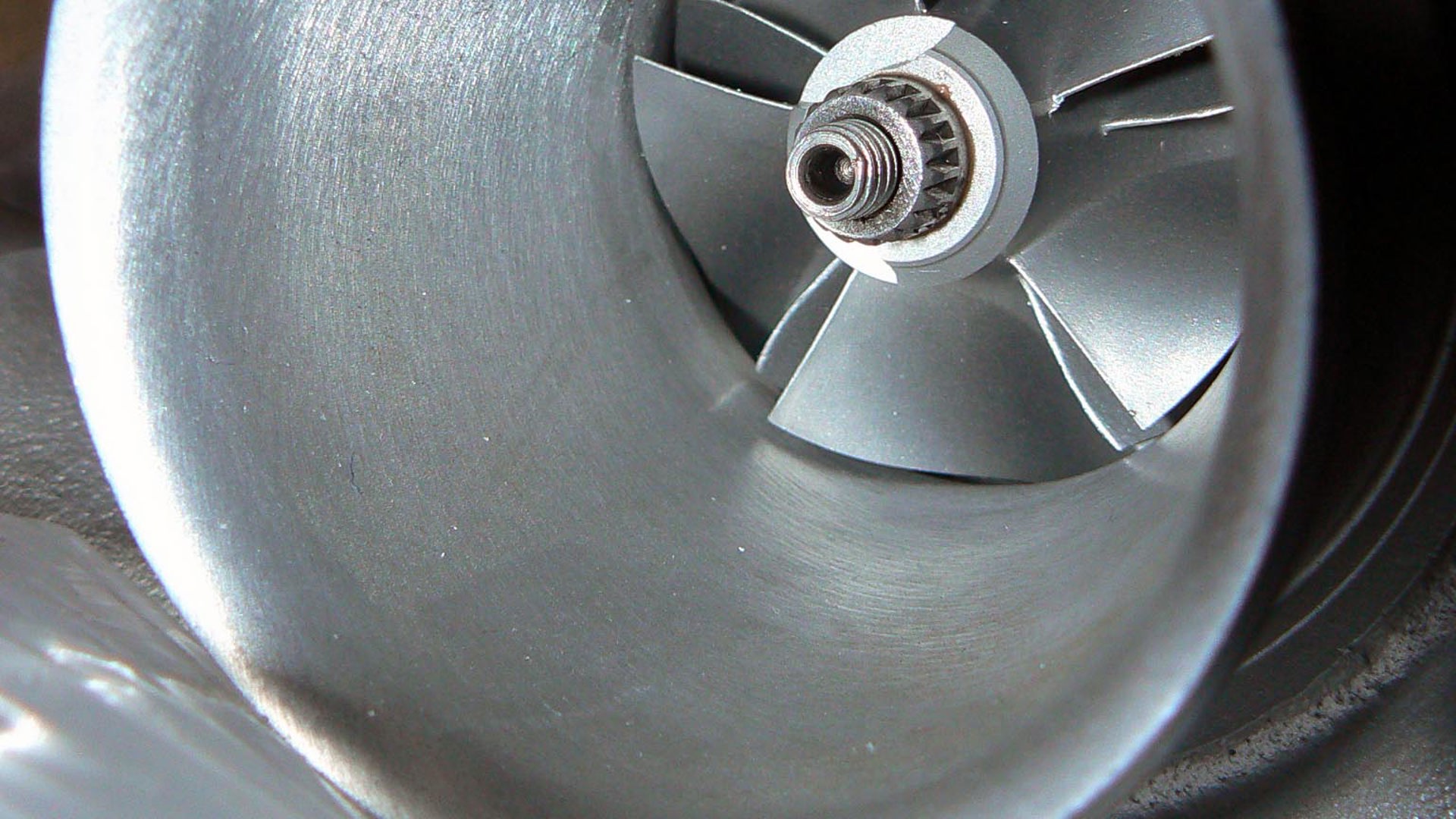
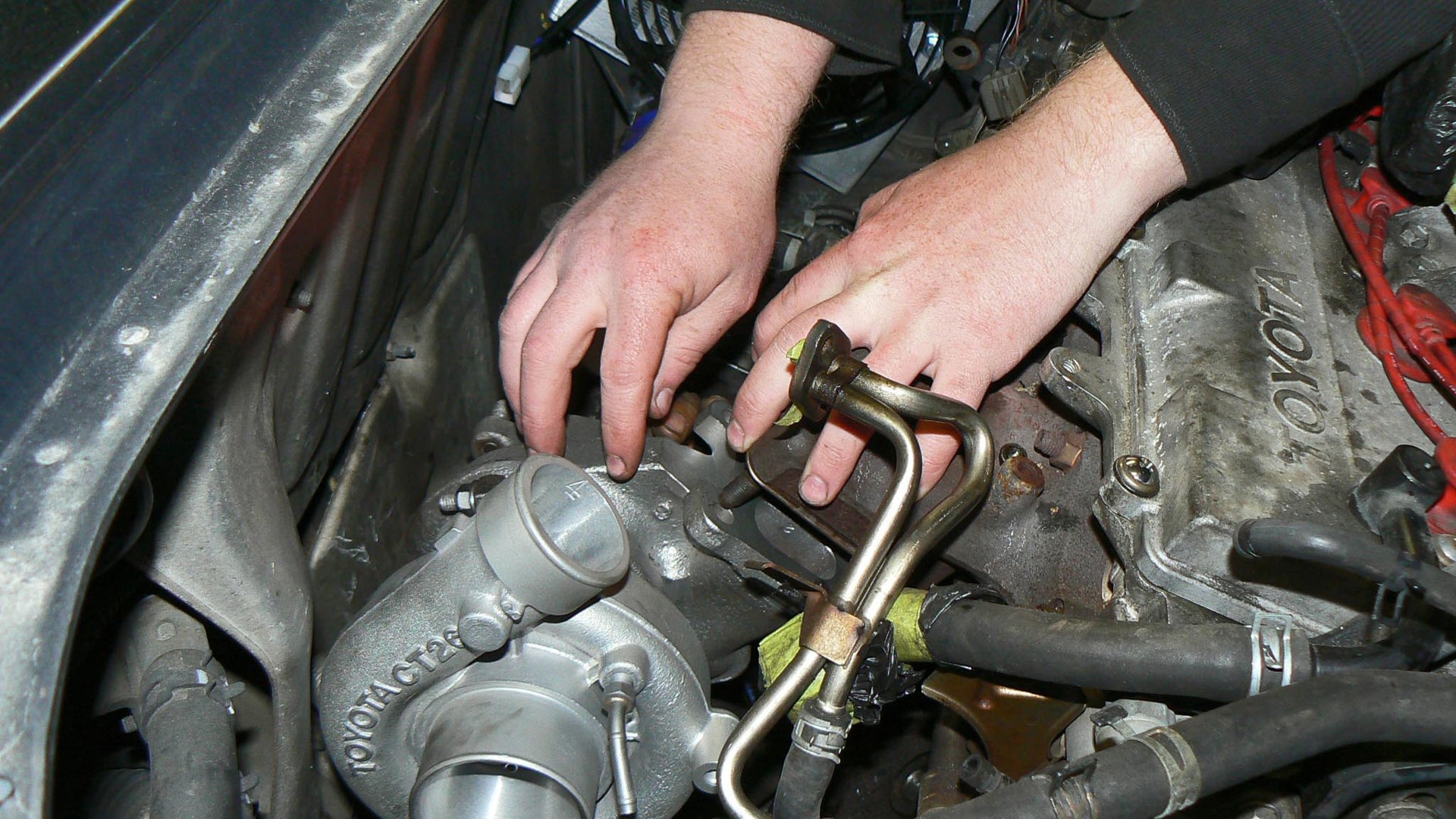
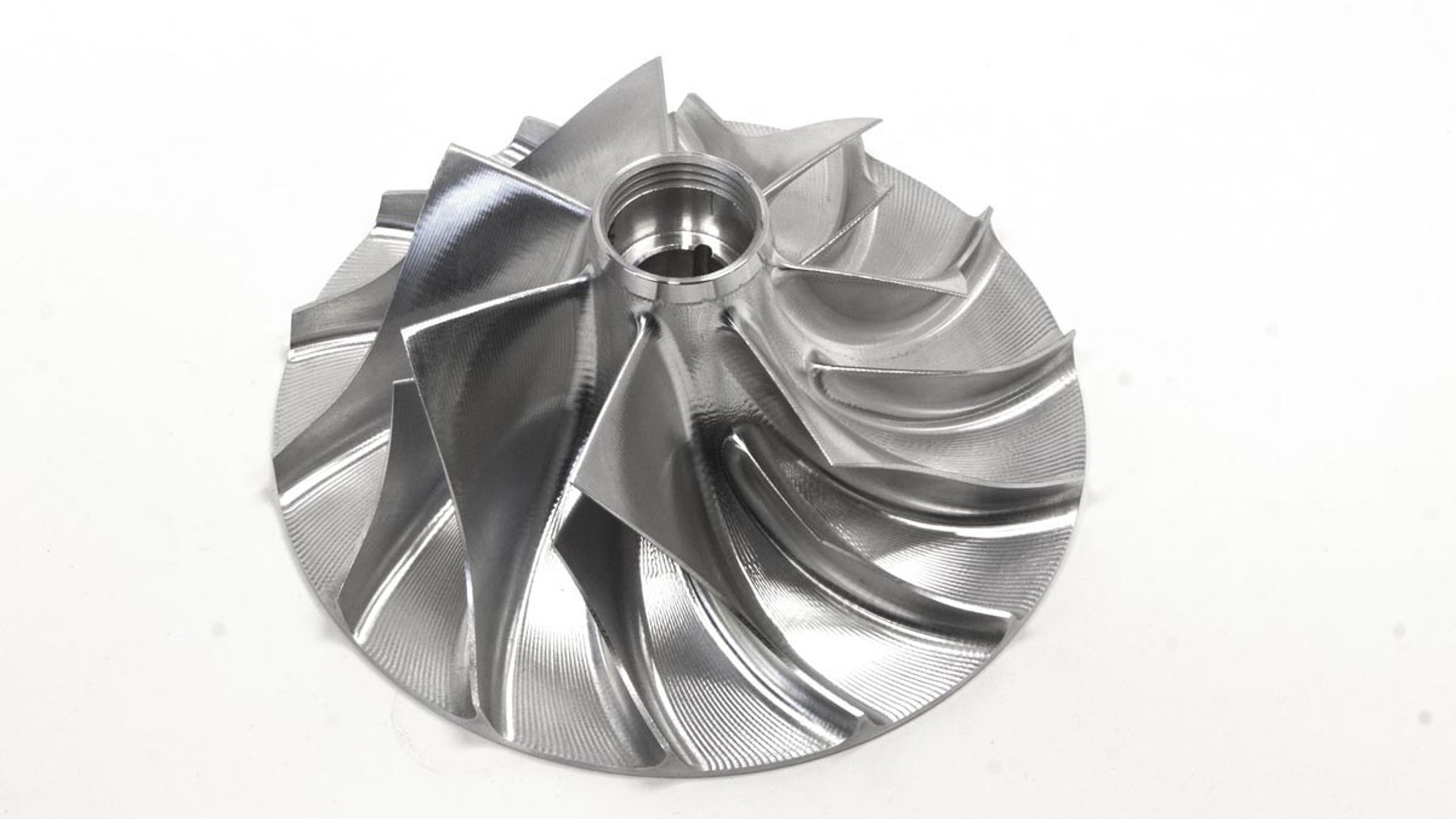
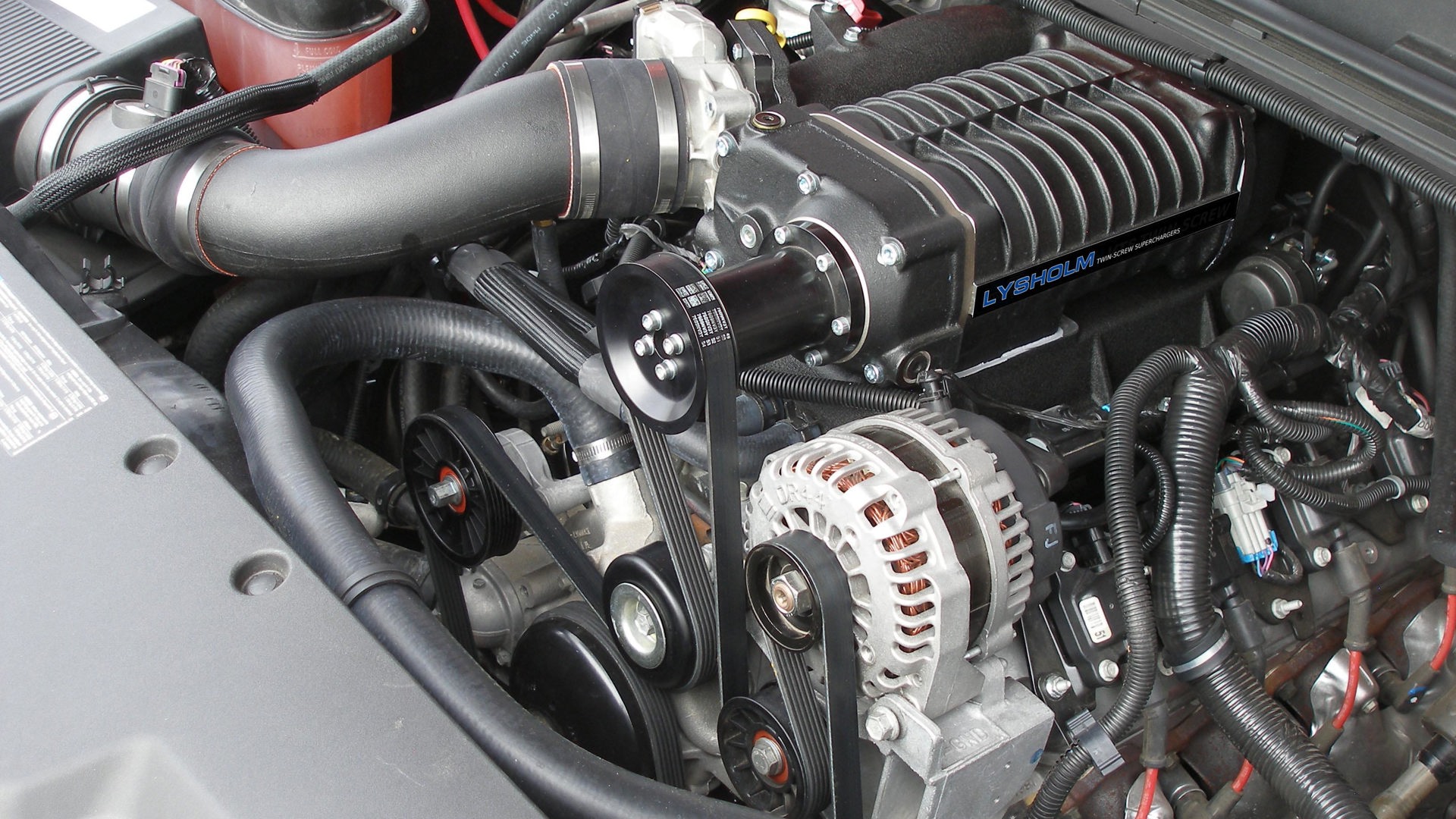
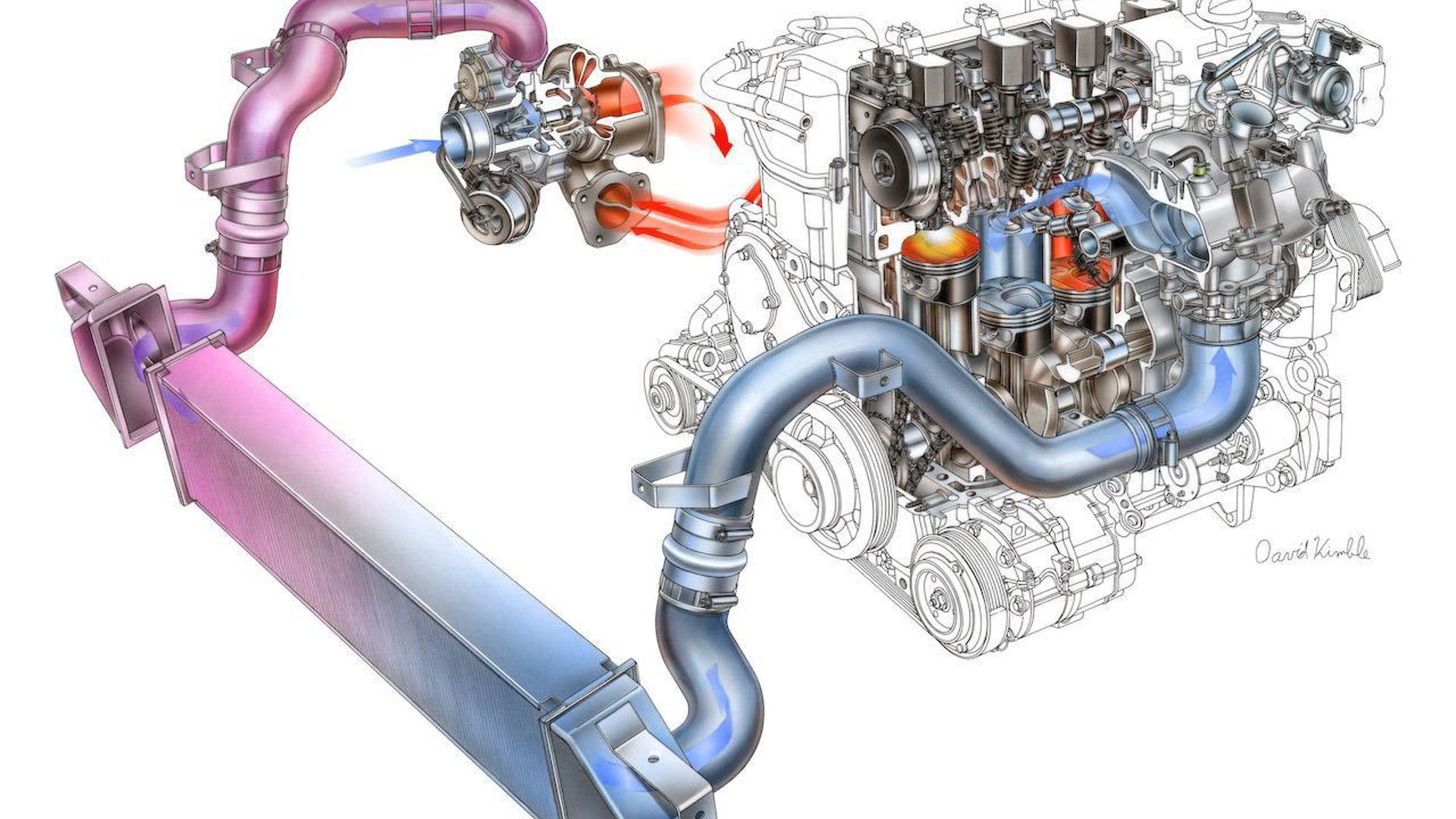
Using a turbocharger or supercharger to ‘boost’ an engine’s power, thereby making a smaller engine perform like a larger one, is one of the oldest go-fast tricks in the book. It’s even more relevant nowadays, as fuel savings are realized by offsetting some of the engine’s output to a turbocharger or supercharger, rather than simply using a bigger, thirstier engine.
Using boost generates the on-demand power drivers want, with reduced fuel consumption when they’re driving gently. In a nutshell, using a smaller, boosted engine instead of a larger one means drivers will burn less fuel, more of the time, with no compromise in performance.
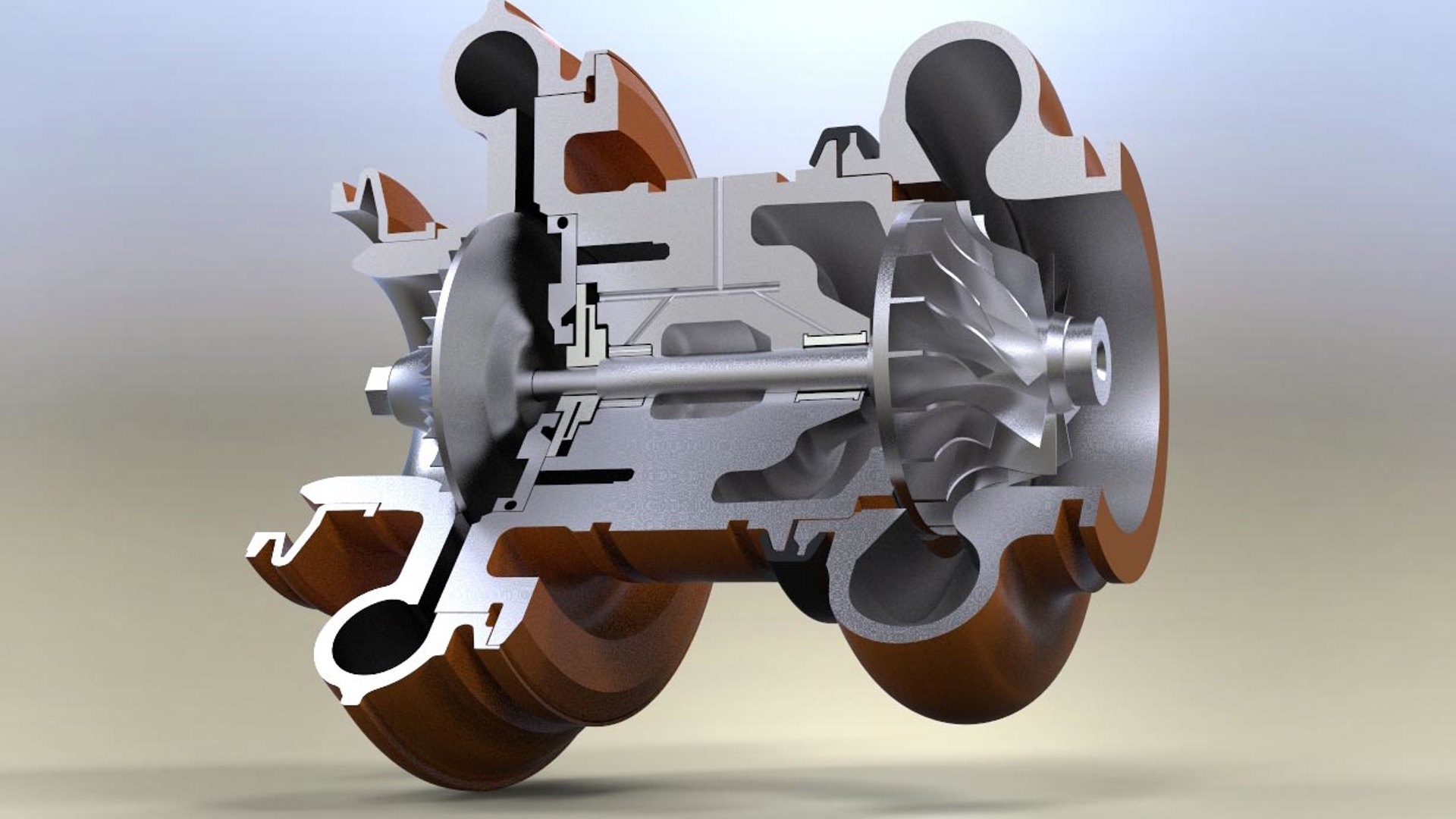
Here’s a closer look at the basics of superchargers, turbochargers, boost and forced induction.